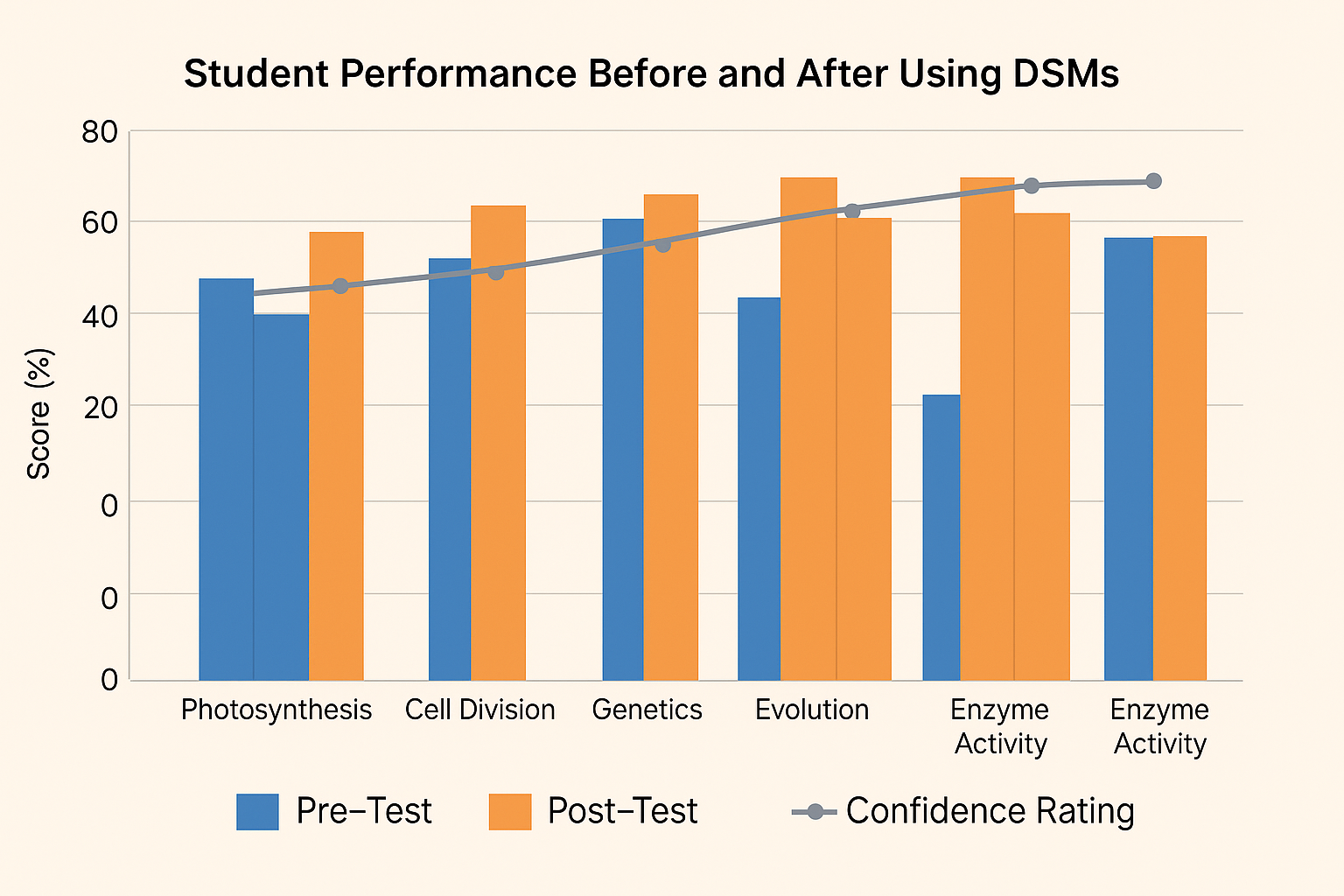
The primary function of Dynamic Study Modules (DSMs) is to help students retain information effectively by continuously adapting content based on their individual knowledge gaps and confidence levels. They use adaptive learning technology to strengthen memory retention and promote long-term learning.
Understanding the Role of Dynamic Study Modules in Learning
What Are Dynamic Study Modules?
Dynamic Study Modules (DSMs) are adaptive learning tools designed to personalize a student’s study experience. Offered by platforms like Mastering Biology and Quizlet, DSMs ask learners to indicate how confident they are about a question before revealing the answer. This lets the module tailor the next set of questions accordingly.
Real-Life Classroom Example:
At Lincoln High School, Mrs. Patel uses DSMs in her biology class. After each lesson, students complete a DSM assignment that helps identify weak areas. The next module then reinforces those specific concepts.
Step-by-Step DSM Activity:
- Students open their learning platform (e.g., Mastering Biology).
- They answer a mix of multiple-choice questions.
- For each answer, they rate their confidence.
- The system adapts the questions in real time.
- Learners revisit difficult topics repeatedly until they master them.
Data to Support:
According to a study by Pearson, students who used DSMs scored 20% higher on retention-based quizzes than those who didn’t.
Sample Dialogue:
Student A: “I thought I knew this topic, but the module showed me what I kept getting wrong.”
Student B: “Same! It kept repeating that question until I got it right confidently.”
Reflection Questions:
- How does feedback-based learning help you improve faster?
- When did you last feel surprised by what you didn’t know?
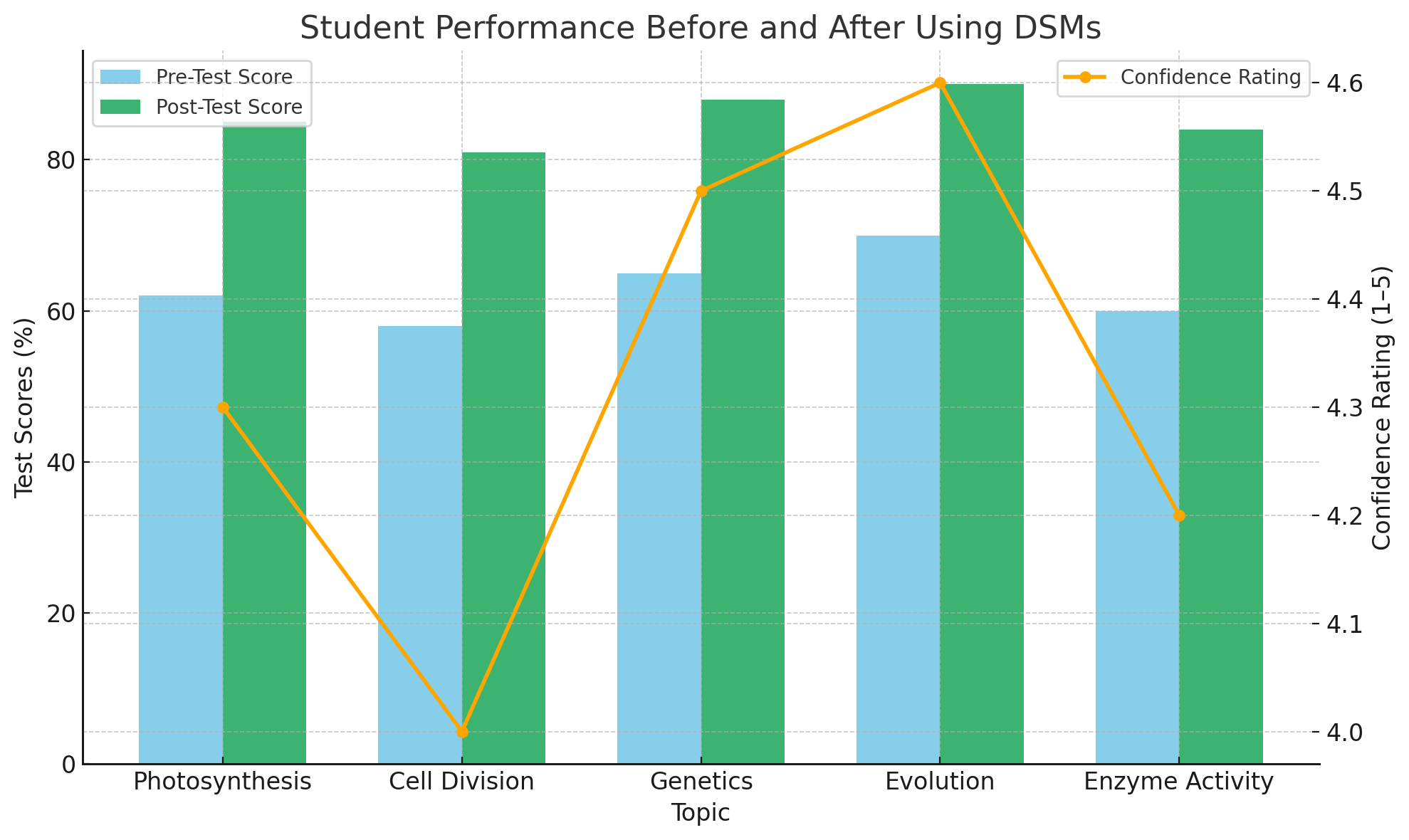
Why Personalization Makes DSMs Powerful
Tailored Learning Paths
Unlike one-size-fits-all study guides, DSMs change based on student responses. They’re designed to be responsive and interactive, so no two learners experience the same module identically.
Classroom Use Case:
At Greenview University, Dr. Lee implemented DSMs in her Human Anatomy course. Students who had varied baseline knowledge felt equally supported. One student, who initially failed the pre-quiz, later topped the final test due to targeted learning via DSMs.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
- Initial diagnostic quiz pinpoints weak areas.
- Confidence scales determine how well students think they know a topic.
- Repetition of weaker topics cements understanding.
- Mastered concepts fade out to save time.
Educational Research:
A 2023 Harvard EdTech study reported that adaptive learning improves retention by up to 35% over static review methods.
Sample Dialogue:
Instructor: “Notice how your DSM is skipping some questions now?”
Student: “Yeah! I guess I mastered those topics.”
Instructor: “Exactly—focus now on the ones it’s still showing!”
Reflection Questions:
- Why is it important to focus more on your weaknesses than your strengths?
- How do confidence scales help in evaluating your knowledge?
Adaptive vs. Traditional Learning
| Aspect | Adaptive Learning | Traditional Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment Type | Continuous, real-time assessments that adjust based on learner responses | Periodic, standardized assessments that do not adapt |
| Feedback Loop | Instant, targeted feedback personalized to learner’s needs | Delayed feedback; often general or one-size-fits-all |
| Time Efficiency | Focuses on areas of weakness, saving time by skipping mastered content | Covers all content uniformly, even what students already understand |
| Student Engagement | High engagement due to personalization and interactivity | Lower engagement, especially for diverse learning speeds or preferences |
DSM and Cognitive Psychology: The Science Behind It
The Spaced Repetition Effect
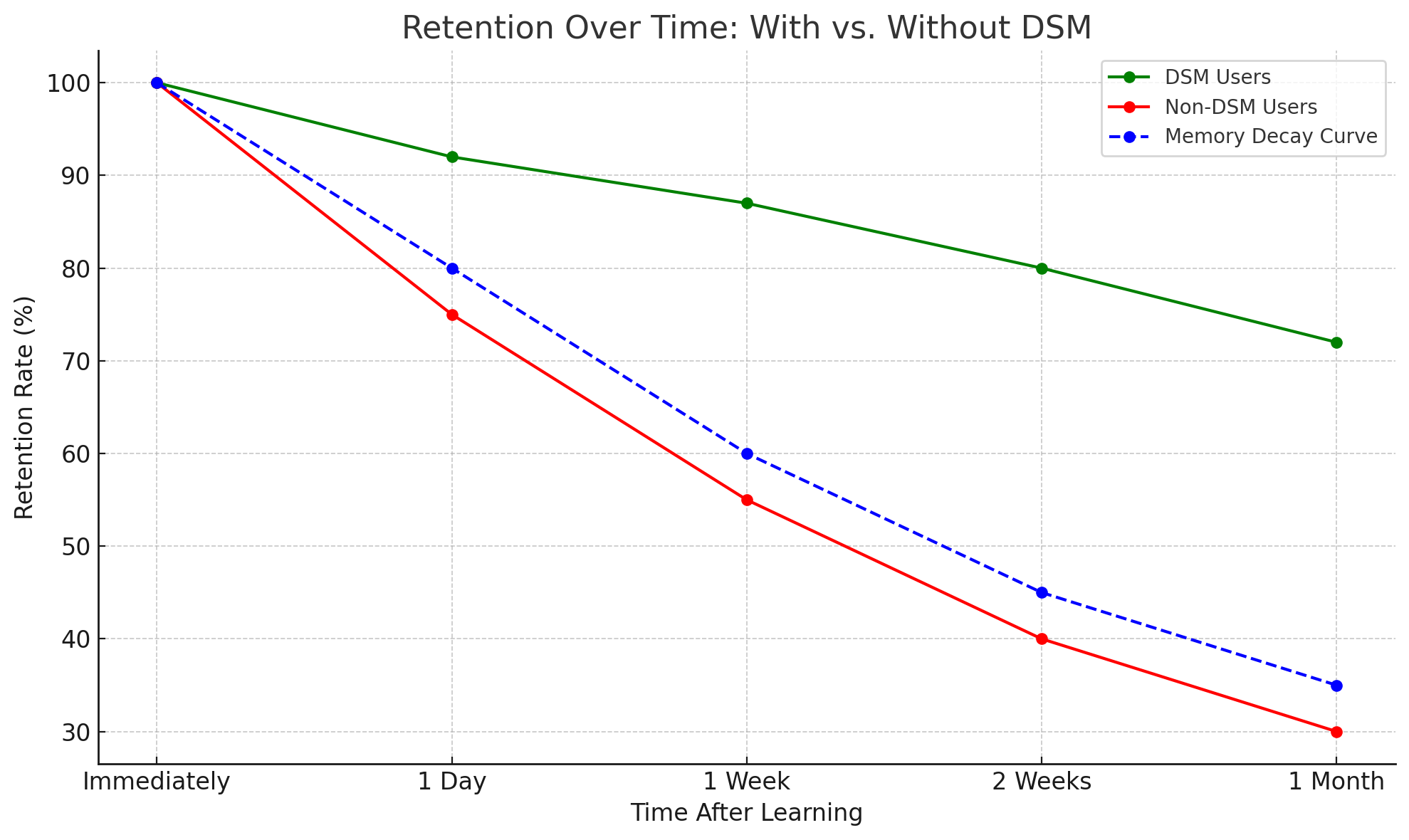
DSMs leverage spaced repetition, a technique rooted in cognitive psychology. This method spaces learning over time and emphasizes the forgetting curve, ensuring concepts are reviewed right before they’re forgotten.
Example from Class:
In Mr. Saunders’ chemistry class, students used DSMs every other day. Over a month, they retained chemical formulas 3x better than a control group using flashcards.
Activity:
- Students complete a module today.
- A similar but slightly different version appears in 2 days.
- Topics resurface in the weekly summary.
- Final assessment confirms mastery.
Study Reference:
The Ebbinghaus forgetting curve shows that without reinforcement, students forget 70% of new material in 24 hours. DSMs intervene just in time.
Sample Dialogue:
Student A: “We learned osmosis last week—why is it in today’s module?”
Student B: “It’s spaced repetition! Helps lock it into long-term memory.”
Reflection Questions:
- When do you tend to forget information the fastest?
- How can repeating info at the right time help you more than constant repetition?
DSM and Growth Mindset: A Winning Combo
Fixed vs. Growth Mindset
A growth mindset means believing intelligence can develop with effort, while a fixed mindset believes abilities are static. DSMs foster growth by encouraging reflection, persistence, and learning from mistakes.
Scenario Sorting Exercise:
Use icons in your eText to:
- Mark when you learn from mistakes (growth).
- Mark when you give up (fixed).
- Mark when you seek help (growth).
Classroom Activity:
- After a tough DSM session, students write about 1 mistake they made.
- They explain what they learned and how they felt.
- Peer sharing helps normalize struggles.
Research Insight:
According to Carol Dweck (Stanford psychologist), students with a growth mindset outperform fixed-mindset peers by up to 50%.
Sample Dialogue:
Teacher: “Why didn’t you skip that tough question?”
Student: “Because I haven’t learned it yet—but I will.”
Reflection Questions:
- How did using “yet” change your attitude toward failure?
- When was a time you grew after struggling?
Growth vs. Fixed Mindset Behaviors
| Behavior Type | Growth Mindset | Fixed Mindset |
|---|---|---|
| Response to Failure | Views failure as a learning opportunity; asks “What can I learn from this?” | Sees failure as a sign of lack of intelligence; gives up easily |
| Effort Belief | Believes effort is essential for mastery and improvement | Believes effort is pointless if you’re not “naturally” good at something |
| Attitude Toward Feedback | Welcomes feedback to grow and improve | Resents or ignores feedback; takes it personally |
Using Mastering to Boost Confidence and Retention
What is the Primary Function in Mastering Biology?
In platforms like Mastering Biology, the primary function of DSMs is to close knowledge gaps through repetition and self-reflection. They also use interleaving—mixing different topics—to improve critical thinking.
Classroom Example:
Prof. Anika in California uses DSMs to prep her class before lectures. Students enter the room with a baseline understanding, which speeds up discussion and deepens engagement.
DSM Access Requirements:
- A valid subscription to Mastering.
- An active course enrollment.
- Compatible browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
- Internet connection.
Step-by-Step Use:
- Log in to Mastering Biology.
- Select assigned DSM.
- Engage with confidence-rated questions.
- Revisit flagged items.
- Review progress dashboard.
Sample Dialogue:
Student: “I never realized how helpful it is to rate my confidence. It makes me think!”
Instructor: “Exactly! Thinking about your thinking is metacognition.”
Reflection Questions:
- Which DSM helped you the most and why?
- What did you discover about how you study best?
Student Feedback on Mastering Biology DSMs
| Feature | Benefit | Satisfaction Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Questioning | Targets weak areas for deeper understanding | 4.6 |
| Immediate Feedback | Reinforces correct answers and clarifies mistakes | 4.8 |
| Personalized Learning Path | Increases engagement and motivation | 4.5 |
| Mobile Accessibility | Enables learning on-the-go | 4.2 |
| Confidence-Based Learning | Helps students self-assess their knowledge accurately | 4.7 |
| Spaced Repetition | Promotes long-term retention | 4.9 |
| Integration with Course Material | Streamlines studying with textbook concepts | 4.4 |
| Visual and Interactive Design | Makes learning more enjoyable and engaging | 4.3 |
FAQs (Search-Optimized)
What is the primary function of Dynamic Study Modules Mastering Biology?
To help students retain core concepts through personalized, adaptive learning that targets knowledge gaps and builds long-term memory.
What are Dynamic Study Modules?
Dynamic Study Modules (DSMs) are AI-driven study tools that adapt in real time based on student performance and confidence, providing repeated exposure to concepts until they’re mastered.
What is the primary function of a concept?
A concept serves as a foundational unit of knowledge, helping learners organize and relate information efficiently across different contexts.
What is the primary function of learning?
The primary function of learning is to acquire, retain, and apply knowledge or skills to solve problems, make decisions, and adapt to new situations.
What is the primary function of Dynamic Study Modules Quizlet?
On Quizlet, DSMs focus on strengthening memory and understanding through interactive flashcards, quizzes, and confidence-based repetition.
What is required to access Dynamic Study Modules?
You’ll need:
- A subscription to platforms like Mastering or Quizlet.
- A compatible device.
- Internet access.
- An instructor-assigned DSM or course enrollment.
What is the primary function of Dynamic Study Modules in Mastering?
To provide adaptive reinforcement of learning, focusing on weak areas, using memory science to boost performance and retention.
What is the primary function of Dynamic Study Modules?
In general, DSMs aim to promote active recall, self-awareness, and mastery of complex topics through repeated, personalized learning.
Which of the following describes a growth mindset, as opposed to a fixed mindset?
- Growth Mindset: Believing that intelligence can be developed through effort.
- Fixed Mindset: Believing that intelligence is a static trait.
Sort each scenario to the eText icon that will help you accomplish that task.
(Example table for students to practice):
Scenario: “I want to review what I missed.” → Use the Highlight icon.
Scenario: “I want to test myself.” → Use the Self-Quiz icon.
Scenario: “I need a summary.” → Use the Notebook icon.
How can you use Mastering to develop a growth mindset and embrace your mistakes?
By viewing mistakes as learning opportunities within DSMs, reflecting on errors, and understanding that persistence leads to growth.
Why is the word “yet” powerful in developing a growth mindset?
It transforms failure into potential. Saying “I don’t understand yet” implies growth is possible, fostering resilience and self-belief.
Final Thoughts
Dynamic Study Modules are more than study aids—they’re brain trainers. From science-backed memory techniques to supporting a growth mindset, they personalize the journey from “I don’t know this” to “I’ve got this!”
Want better grades without the burnout?
Start using DSMs today and unlock your learning potential.
🧠💡 Ready to make study time smart time? Share your DSM experience in the comments!