How to Study Korean: Great Guide for Beginners in 2026
How can someone study Korean effectively as a beginner?
To study Korean effectively, start by learning Hangul (the Korean alphabet), then build a strong foundation in basic grammar, essential vocabulary, and pronunciation. Use language apps, online courses, flashcards, and native content like K-dramas or Korean songs to boost listening and speaking skills. This guide provides a structured roadmap—from beginner to advanced—with proven strategies, daily practice tips, and the best free and paid resources to help you learn Korean quickly and confidently.
Introduction
Korean is one of the fastest-growing languages in the world, attracting millions of learners due to its cultural significance, economic opportunities, and the global popularity of K-pop and K-dramas. Whether you want to understand your favorite Korean songs, communicate fluently while traveling in South Korea, or expand your career opportunities, learning Korean can be an incredibly rewarding experience. However, many beginners struggle with where to start and how to study Korean.

Unlike English and other Latin-based languages, Korean has a unique writing system, distinct sentence structure, and honorifics that can make it seem challenging at first. But with the right approach and consistent effort, anyone can achieve fluency. This guide is designed to help you build a solid foundation in Korean, offering a structured learning plan that ensures long-term retention and practical application.
Why Should You Learn Korean?
Korean is more than just a language; it is the key to understanding a vibrant culture and connecting with over 80 million native speakers worldwide. Here are some compelling reasons why learning Korean is worth the effort:
- Cultural Access and Entertainment – Korean entertainment, including music, films, and television dramas, has a global fanbase. By learning the language, you can fully appreciate the nuances of K-pop lyrics, enjoy K-dramas without subtitles, and engage with Korean literature and webtoons.
- Career Opportunities – With South Korea being one of the world's largest economies, proficiency in Korean can open doors in industries such as technology, finance, and international business. Many multinational corporations, including Samsung, Hyundai, and LG, actively seek bilingual professionals who can bridge the gap between Korean and global markets.
- Travel and Communication – South Korea is a popular tourist destination known for its rich history, modern cities, and culinary experiences. Learning basic Korean phrases enhances your travel experience, allowing you to interact with locals, navigate transportation, and enjoy authentic cultural exchanges.
- Cognitive and Educational Benefits – Learning a new language sharpens cognitive abilities, improves memory, and enhances problem-solving skills. The structured nature of the Korean language, particularly its systematic writing system (Hangul), makes it an excellent choice for linguistic enthusiasts.
What Makes Korean Different from Other Languages?
Korean stands out due to its unique linguistic features, which can be both an advantage and a challenge for new learners:
- Hangul: The Scientific Writing System – Unlike Chinese and Japanese, which rely on thousands of complex characters, Korean uses Hangul, a phonetic alphabet consisting of just 24 letters. It was designed in the 15th century to be logical and easy to learn, making it one of the most accessible writing systems for beginners.
- Sentence Structure (SOV vs. SVO) – English follows a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) structure ("I eat food"), whereas Korean follows a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) structure ("I food eat"). Adjusting to this syntax is essential for mastering Korean sentence formation.
- Honorifics and Formality Levels – Korean has multiple speech levels that dictate how you address others based on age, status, and social hierarchy. Understanding when to use formal vs. informal language is crucial for effective communication.
- Borrowed and Native Vocabulary – Korean contains many words borrowed from Chinese and English, making it easier for learners with prior knowledge of these languages to recognize some vocabulary.
How This Guide Will Help You Learn Korean Efficiently
Many beginners fall into the trap of studying Korean without a structured approach, leading to frustration and slow progress. This guide provides a step-by-step learning strategy, ensuring that you build skills in the correct order—starting from Hangul and basic vocabulary, progressing to grammar and sentence formation, and eventually refining your listening and speaking abilities.
Throughout this guide, you will discover:
- The most effective ways to learn Hangul in a short time.
- Practical vocabulary-building techniques that enhance retention.
- Essential grammar rules and sentence structures to form correct expressions.
- Proven listening and speaking methods to develop fluency.
- The best online resources, apps, and courses to accelerate your learning journey.
By following this structured approach, you will gain a deep understanding of the Korean language and culture while avoiding common pitfalls that slow down progress. Whether you are a complete beginner or have some prior experience, this guide will help you advance toward fluency in the most efficient way possible.
Now, let’s get started with the first and most fundamental step—learning Hangul, the Korean alphabet.
Step 1: Learn Hangul (The Korean Alphabet) Quickly and Effectively
Why Learning Hangul Is Essential
Many beginners attempt to learn Korean by memorizing Romanized words and phrases. However, this approach significantly hinders progress. The most effective way to start learning Korean is by mastering Hangul, the Korean alphabet. Unlike English, which uses Latin letters, or Chinese and Japanese, which rely on thousands of complex characters, Hangul is a scientifically designed phonetic writing system that is easy to learn.

Developed in the 15th century by King Sejong the Great, Hangul was designed to be logical and accessible, enabling people of all social classes to read and write with ease. It consists of just 24 letters (14 consonants and 10 vowels), making it one of the most efficient writing systems in the world.
How Long Does It Take to Learn Hangul?
Most learners can grasp Hangul within a day or two with the right strategy. Unlike English, where pronunciation can be inconsistent, Hangul follows clear phonetic rules. Once you learn the letters, you can immediately start reading Korean words, even if you don’t yet understand their meanings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Learning Hangul
1. Understand the Structure of Hangul
Hangul letters are grouped into syllabic blocks, rather than being written in a straight line like English. Each syllabic block consists of:
- A consonant (beginning sound)
- A vowel (middle sound)
- An optional final consonant (ending sound)
For example:
- 가 (ga) → ㄱ (g/k) + ㅏ (a)
- 한 (han) → ㅎ (h) + ㅏ (a) + ㄴ (n)
2. Learn the 14 Basic Consonants
Korean consonants are inspired by the shape of the mouth and tongue when pronouncing them:
| Hangul | Romanization | Approximate English Sound |
|---|---|---|
| ㄱ | g/k | g in "go" or k in "kite" |
| ㄴ | n | n in "nose" |
| ㄷ | d/t | d in "dog" or t in "top" |
| ㄹ | r/l | Between r and l sound |
| ㅁ | m | m in "moon" |
| ㅂ | b/p | b in "boy" or p in "pool" |
| ㅅ | s | s in "snake" |
| ㅇ | silent/ng | Silent at beginning, ng at end |
| ㅈ | j | j in "jump" |
| ㅊ | ch | ch in "cheese" |
| ㅋ | k | k in "kick" |
| ㅌ | t | t in "table" |
| ㅍ | p | p in "park" |
| ㅎ | h | h in "hello" |
3. Learn the 10 Basic Vowels
Korean vowels are simple to recognize and combine with consonants:
| Hangul | Romanization | Approximate English Sound |
|---|---|---|
| ㅏ | a | a in "car" |
| ㅑ | ya | ya in "yard" |
| ㅓ | eo | o in "son" |
| ㅕ | yeo | yo in "yawn" |
| ㅗ | o | o in "go" |
| ㅛ | yo | yo in "yoga" |
| ㅜ | u | oo in "moon" |
| ㅠ | yu | u in "cute" |
| ㅡ | eu | u in "put" |
| ㅣ | i | ee in "tree" |
4. Master Double Consonants and Complex Vowels
Once you are comfortable with basic Hangul letters, you should learn double consonants (tense sounds) and complex vowels (diphthongs).
Double Consonants:
| Hangul | Romanization | Approximate Sound |
|---|---|---|
| ㄲ | kk | Strong "k" sound |
| ㄸ | tt | Strong "t" sound |
| ㅃ | pp | Strong "p" sound |
| ㅆ | ss | Strong "s" sound |
| ㅉ | jj | Strong "j" sound |
Complex Vowels:
| Hangul | Romanization | Approximate Sound |
|---|---|---|
| ㅐ | ae | a in "cat" |
| ㅒ | yae | ya in "yam" |
| ㅔ | e | e in "net" |
| ㅖ | ye | ye in "yes" |
| ㅘ | wa | wa in "wand" |
| ㅙ | wae | wae in "wait" |
| ㅚ | oe | we in "wet" |
| ㅝ | wo | wo in "wonder" |
| ㅞ | we | we in "wet" |
| ㅟ | wi | we in "week" |
| ㅢ | ui | ui in "oui" (French) |
5. Practice Reading and Writing Hangul
Once you recognize the letters, start forming syllabic blocks and reading simple words. Some practical exercises include:
- Reading signs and menus in Korean
- Writing your name in Hangul
- Typing in Korean (Use Korean keyboard settings)
- Practicing with flashcards (Anki, Quizlet)
6. Use the Best Online Resources to Learn Hangul
Several tools and platforms can help accelerate your Hangul learning process:
- Duolingo (Gamified Hangul lessons)
- Talk to Me in Korean (TTMIK) (Free beginner-friendly lessons)
- Memrise (Interactive vocabulary practice)
- How to Study Korean (Comprehensive grammar explanations)
- Hangul Worksheets (Downloadable writing practice sheets)
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning Hangul
- Skipping Hangul and relying on Romanization – This slows down progress and affects pronunciation.
- Not practicing reading out loud – Sounding out words improves retention and pronunciation.
- Ignoring stroke order – Writing Hangul correctly ensures better readability.
- Learning words without understanding syllable structure – Breaking words into blocks helps with accurate pronunciation.
The Key to Mastering Hangul
Learning Hangul is the foundation of studying Korean. Once you become comfortable reading and writing Hangul, everything else—vocabulary, grammar, speaking, and listening—becomes significantly easier. By dedicating a few focused study sessions, you can fully grasp Hangul and start reading real Korean words within days.
With Hangul mastered, the next step is expanding your Korean vocabulary and building essential phrases, which we will cover in the next section.
Step 2: Build a Strong Korean Vocabulary Foundation
Why Expanding Your Korean Vocabulary is Crucial
Once you have mastered Hangul, the next essential step is building a strong vocabulary foundation. Vocabulary is the backbone of language learning—without enough words, you won’t be able to form sentences, understand conversations, or express yourself effectively.

For beginners, learning the right set of words is more important than memorizing random vocabulary. A strategic approach, focusing on high-frequency words, essential phrases, and topic-based vocabulary, will significantly accelerate your progress.
How Many Words Do You Need to Know?
The number of words needed to achieve fluency varies, but here’s a general guideline:
- 500 words – You can hold basic conversations and understand common phrases.
- 1,000 words – You can express yourself in everyday situations.
- 2,000–3,000 words – You can read and understand most casual texts.
- 5,000+ words – You can engage in deep conversations and read advanced content.
Since Korean is a context-heavy language, learning words in phrases and sentences rather than isolation helps you use them correctly in real situations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Learning Korean Vocabulary
1. Start with the Most Common Korean Words
To maximize efficiency, focus on high-frequency words that appear in everyday conversations. Here’s a categorized list to get started:
Common Korean Nouns (명사 - Myeongsa)
| Hangul | Romanization | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 사람 | saram | person |
| 친구 | chingu | friend |
| 가족 | gajok | family |
| 음식 | eumsik | food |
| 집 | jip | house/home |
| 학교 | hakgyo | school |
| 일 | il | work/job |
| 시간 | sigan | time |
| 돈 | don | money |
| 사랑 | sarang | love |
Essential Korean Verbs (동사 - Dongsa)
| Hangul | Romanization | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 하다 | hada | to do |
| 먹다 | meokda | to eat |
| 마시다 | masida | to drink |
| 가다 | gada | to go |
| 오다 | oda | to come |
| 보다 | boda | to see/watch |
| 듣다 | deutda | to listen |
| 말하다 | malhada | to speak |
| 배우다 | baeuda | to learn |
| 좋아하다 | joahada | to like |
Basic Korean Adjectives (형용사 - Hyeongyongsa)
| Hangul | Romanization | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 크다 | keuda | big |
| 작다 | jakda | small |
| 예쁘다 | yeppeuda | pretty |
| 빠르다 | ppareuda | fast |
| 느리다 | neurida | slow |
| 쉽다 | swipda | easy |
| 어렵다 | eoryeopda | difficult |
| 맛있다 | masitda | delicious |
| 비싸다 | bissada | expensive |
| 싸다 | ssada | cheap |
2. Learn Useful Korean Phrases for Everyday Use
Once you have a basic vocabulary, start practicing useful phrases to build fluency.
Common Greetings & Polite Expressions
| Hangul | Romanization | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 안녕하세요 | annyeonghaseyo | Hello |
| 감사합니다 | gamsahamnida | Thank you |
| 죄송합니다 | joesonghamnida | I'm sorry |
| 괜찮아요 | gwaenchanayo | It's okay |
| 반갑습니다 | bangapseumnida | Nice to meet you |
Basic Conversational Phrases
| Hangul | Romanization | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 이름이 뭐예요? | ireumi mwoyeyo? | What’s your name? |
| 저는 ___입니다. | jeoneun ___imnida. | I am ___ (your name). |
| 어디에서 왔어요? | eodieseo wasseoyo? | Where are you from? |
| 한국어 할 수 있어요? | hangugeo hal su isseoyo? | Can you speak Korean? |
| 얼마예요? | eolmayeyo? | How much is this? |
3. Use Spaced Repetition to Memorize Words Efficiently
Rote memorization is ineffective for long-term retention. Instead, use spaced repetition techniques (SRS) to reinforce vocabulary over time. Apps like Anki, Memrise, or Quizlet are excellent tools for this.
🔹 How Spaced Repetition Works:
- Words you struggle with appear more frequently.
- Words you already know well appear less often.
- This helps reinforce learning while avoiding unnecessary repetition.
4. Read and Listen to Korean Daily
Passive exposure is just as important as active study. Incorporating reading and listening practice into your daily routine will accelerate vocabulary acquisition.
Best Resources for Reading Korean
- Naver Dictionary – Look up words with example sentences.
- Webtoons (네이버 웹툰) – Comics with casual conversation styles.
- Children’s Books – Simple sentence structures make learning easier.
- Korean Blogs & News Websites – Try Naver News or Daum News.
Best Resources for Listening Practice
- Korean Dramas & Movies – Watch with Korean subtitles to reinforce vocabulary.
- K-Pop Songs – Look up lyrics and sing along.
- Podcasts & YouTube Channels – Channels like Talk To Me In Korean (TTMIK) provide structured lessons.
- Korean Audiobooks – Platforms like Audioclip (by Naver) offer free content.
5. Speak and Write in Korean Every Day
To truly internalize vocabulary, you must use it daily in writing and conversation.
Writing Practice:
- Journaling – Write a few sentences in Korean daily.
- Social Media Posts – Try tweeting or posting in Korean.
- Chat with AI Bots – Apps like HelloTalk or Tandem provide native speaker interactions.
Speaking Practice:
- Language Exchange – Partner with native Korean speakers via HelloTalk, iTalki, or Speaky.
- Shadowing Technique – Listen to Korean sentences and repeat them.
- Join Online Korean Communities – Engaging in discussions improves retention.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning Vocabulary
🔸 Memorizing words without context – Always learn words within sentences.🔸 Not practicing pronunciation – Use apps with native audio to refine your accent.🔸 Trying to learn too many words at once – Focus on 20–30 words per week for better retention.🔸 Skipping review sessions – Regular review is key to long-term memory.
The Key to Building a Strong Korean Vocabulary
Expanding your vocabulary is a gradual process that requires consistent practice and strategic learning methods. By focusing on high-frequency words, using spaced repetition, and immersing yourself in real Korean content, you will steadily increase your fluency.
Once you have a solid vocabulary base, the next crucial step is understanding Korean grammar—which we will cover in the next section.
Step 3: Mastering Korean Grammar for Fluent Communication
Why Korean Grammar is Essential
Once you have built a solid vocabulary base, the next critical step in your Korean language learning journey is understanding grammar. Unlike English, Korean follows a unique sentence structure and has different levels of formality that affect communication. Without a firm grasp of grammar, even a strong vocabulary will not be enough to form coherent and natural sentences.

Korean grammar may seem challenging at first, but with the right approach, you can master it efficiently. This section will break down sentence structure, essential grammatical rules, verb conjugation, particles, and honorifics to help you construct meaningful sentences in Korean.
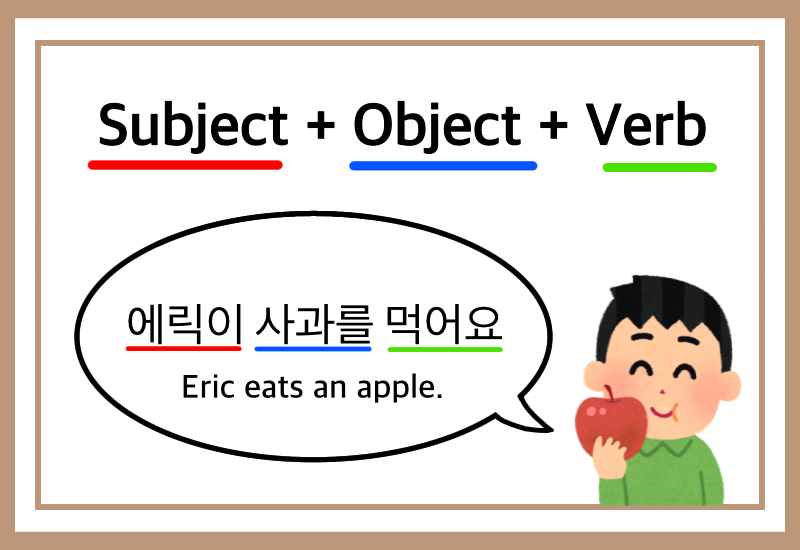
1. Understanding Korean Sentence Structure (SOV vs. SVO)
One of the biggest differences between English and Korean is sentence structure.
English follows Subject-Verb-Object (SVO):
- "I eat an apple."
Korean follows Subject-Object-Verb (SOV):
- "나는 사과를 먹어요." (Naneun sagwareul meogeoyo.)
- Literal translation: "I an apple eat."
This means that in Korean, the verb always comes at the end of the sentence. Understanding this structure is the foundation of Korean grammar.
🔹 Basic Korean Sentence Formula:
[Subject] + [Object] + [Verb]
✅ 나는 책을 읽어요. (Naneun chaekeul ilgoyo.) → "I read a book."
✅ 그는 한국어를 공부해요. (Geuneun hangugeoreul gongbuhaeyo.) → "He studies Korean."
2. The Role of Particles in Korean Grammar
Korean uses particles to indicate the subject, object, and other parts of speech. These particles do not exist in English, so understanding their function is crucial.
Common Korean Particles and Their Functions
| Particle | Usage | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 은/는 | Topic marker | 저는 학생이에요. (Jeoneun haksaeng-ieyo.) | "I am a student." |
| 이/가 | Subject marker | 날씨가 좋아요. (Nalssiga joayo.) | "The weather is good." |
| 을/를 | Object marker | 책을 읽어요. (Chaekeul ilgoyo.) | "I read a book." |
| 에 | Location/time marker | 학교에 가요. (Hakgyoe gayo.) | "I go to school." |
| 에서 | Location of action | 집에서 공부해요. (Jibeseo gongbuhaeyo.) | "I study at home." |
| 와/과, 하고, (이)랑 | "And" (connector) | 친구와 놀아요. (Chinguwa norayo.) | "I play with my friend." |
| 도 | "Also" or "Too" | 저도 한국어를 공부해요. (Jeodo hangugeoreul gongbuhaeyo.) | "I also study Korean." |
🔹 Key Tip: Particles can be tricky because they change depending on whether the word ends in a consonant or vowel. 은/는 and 이/가 are often confused, but 은/는 is used for general topics, while 이/가 emphasizes the subject of the sentence.
3. Korean Verb Conjugation: Present, Past, and Future
Korean verbs do not change based on the subject (I, you, he, she, etc.), but they do conjugate based on tense and politeness level.
Present Tense
To conjugate a verb in the present tense, you need to add -아요 (-ayo) or -어요 (-eoyo) to the verb stem:
| Base Verb | Meaning | Conjugated Form | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 가다 (gada) | To go | 가요 (gayo) | 저는 학교에 가요. ("I go to school.") |
| 먹다 (meokda) | To eat | 먹어요 (meogeoyo) | 나는 밥을 먹어요. ("I eat rice.") |
| 마시다 (masida) | To drink | 마셔요 (mashyeoyo) | 커피를 마셔요. ("I drink coffee.") |
Past Tense
For past tense, the verb stems take -았어요 (-asseoyo) or -었어요 (-eosseoyo):
| Base Verb | Meaning | Conjugated Form | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 가다 | To go | 갔어요 (gasseoyo) | 저는 학교에 갔어요. ("I went to school.") |
| 먹다 | To eat | 먹었어요 (meogeosseoyo) | 나는 밥을 먹었어요. ("I ate rice.") |
Future Tense
For future tense, use -(으)ㄹ 거예요 (-eul geoyeyo):
| Base Verb | Meaning | Conjugated Form | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 가다 | To go | 갈 거예요 (gal geoyeyo) | 저는 내일 갈 거예요. ("I will go tomorrow.") |
| 먹다 | To eat | 먹을 거예요 (meogeul geoyeyo) | 나는 저녁을 먹을 거예요. ("I will eat dinner.") |
4. Honorifics and Formality Levels in Korean
Korean has different levels of politeness that affect verb endings and word choice. It’s essential to use the correct form depending on who you are speaking to.
Three Main Speech Levels in Korean:
| Level | Usage | Example Sentence (Verb: to eat) |
|---|---|---|
| Formal (합니다) | Business, presentations | 밥을 먹습니다. (Bapeul meokseumnida.) |
| Polite (해요) | Everyday conversations | 밥을 먹어요. (Bapeul meogeoyo.) |
| Casual (해) | Friends, younger people | 밥을 먹어. (Bapeul meogeo.) |
🔹 Tip: If you're unsure which form to use, stick with the polite 해요 (haeyo) form, as it's widely accepted in most situations.
5. Sentence Construction: Putting It All Together
Now that we understand sentence structure, particles, verb conjugation, and politeness levels, let’s construct a complete sentence.
Example Sentence Breakdown
🔹 English: "Yesterday, I ate delicious Korean food at a restaurant with my friend."
🔹 Korean Sentence:👉 어제 친구와 식당에서 맛있는 한국 음식을 먹었어요.(Eoje chinguwa sikdang-eseo masinneun hanguk eumsigeul meogeosseoyo.)
🔹 Breaking it down:
- 어제 (eoje) – Yesterday (time marker)
- 친구와 (chinguwa) – With my friend (connector 와 for "and/with")
- 식당에서 (sikdang-eseo) – At a restaurant (location marker 에서)
- 맛있는 (masinneun) – Delicious (adjective modifying food)
- 한국 음식 (hanguk eumsik) – Korean food
- 을 (eul) – Object marker
- 먹었어요 (meogeosseoyo) – Ate (past tense verb)
Why Mastering Grammar is Essential for Fluency
Mastering Korean grammar is not about memorization—it’s about understanding patterns and applying them in real conversations. By learning sentence structure, particles, verb conjugation, and formality levels, you can start forming your own sentences with confidence.
Now that you have a strong grasp of Korean grammar, the next step is improving your listening and speaking skills, which we will cover in the next section.
Step 4: Enhancing Listening and Speaking Skills in Korean
After mastering Korean grammar, the next crucial step is developing strong listening and speaking skills. These skills are essential for real-life communication and understanding native speakers, whether in conversations, media, or formal settings.

Unlike reading and writing, which allow you time to process information, listening and speaking require quick thinking, comprehension, and proper pronunciation. This section will guide you through effective listening techniques, pronunciation practice, and conversation strategies to improve your fluency in Korean.
1. Improving Your Korean Listening Skills
Listening is the foundation of verbal communication. The more you expose yourself to spoken Korean, the faster your comprehension improves. Here’s how to enhance your listening skills:
A. Start with Beginner-Friendly Korean Content
Beginners should start with slow, clear, and simple Korean audio before moving to faster, natural speech.
🔹 Recommended Resources for Beginners:
- Talk To Me In Korean (TTMIK) – Beginner-friendly Korean podcasts.
- Korean dramas with subtitles – Start with English subtitles, then switch to Korean.
- YouTube channels like Korean Unnie and Learn Korean with GO! Billy Korean.
- Slow Korean news – Websites like KBS World Radio offer news in slow Korean.
B. Use Active Listening Techniques
Passive listening (playing audio in the background) is helpful, but active listening is more effective.
✅ Step 1: Listen Once for General Meaning
- Don't focus on every word; try to understand the main idea.
✅ Step 2: Replay and Identify Keywords
- Listen again and pick out familiar words or phrases.
✅ Step 3: Read Along with Transcripts
- Use resources like TTMIK or KoreanClass101, which provide audio with transcripts.
✅ Step 4: Shadowing Practice
- Shadowing means listening to Korean speech and repeating it immediately without pausing.
- This trains your brain to process sounds faster and improves pronunciation.
2. Perfecting Korean Pronunciation
Proper pronunciation is key to being understood by native speakers. Since Korean has sounds that do not exist in English, mastering pronunciation requires dedicated practice.
A. Focus on Difficult Korean Sounds
Korean has several tricky consonants and vowels.
| Korean Sound | Common Pronunciation Challenge | Example Words |
|---|---|---|
| ㅂ, ㄷ, ㄱ (Basic Sounds) | Similar to b, d, g in English | 바다 (bada) – Ocean |
| ㅃ, ㄸ, ㄲ (Tense Sounds) | Requires extra pressure in pronunciation | 빵 (ppang) – Bread |
| ㅍ, ㅌ, ㅋ (Aspirated Sounds) | Sounds like p, t, k with a strong burst of air | 커피 (keopi) – Coffee |
| 으 (eu) | Does not exist in English, often mispronounced as "oo" | 크다 (keuda) – Big |
🔹 Tip: Use the IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) for Korean sounds and compare them with native speakers on sites like Forvo.
B. Record Yourself Speaking
- Use a voice recording app to compare your pronunciation with native speakers.
- Mimic Korean drama actors and YouTubers to copy their intonation.
C. Practice with a Native Speaker
- Find language partners on apps like HelloTalk, Tandem, or Italki.
- Join Korean conversation groups in your local community or online.
3. Engaging in Korean Conversations
Speaking confidently in Korean requires real interaction. The best way to develop fluency is by actively using the language in daily conversations.
A. Start with Basic Daily Conversations
Practicing simple daily dialogues helps you gain confidence before moving to complex topics.
🔹 Common Conversation Topics:
✅ Introducing Yourself – “안녕하세요? 저는 [이름]이에요.” (Hello, I am [Name].)
✅ Ordering Food – “김밥 하나 주세요.” (One kimbap, please.)
✅ Asking for Directions – “화장실이 어디에 있어요?” (Where is the restroom?)
✅ Shopping in Korea – “이거 얼마예요?” (How much is this?)
B. Use the 3-Second Rule
If you're stuck while speaking, try to respond within three seconds—even if it’s not perfect.
- Instead of translating from English, use simple Korean phrases.
- Example: If you forget the word for "restaurant," say “밥 먹는 곳” (the place to eat rice) instead of switching to English.
C. Use AI and Language Exchange Apps
✅ Speech-to-text apps like Papago can check pronunciation.
✅ AI-based apps like ChatGPT or TalkPal can simulate real conversations.
✅ Italki, HelloTalk, and Tandem connect you with native speakers.
4. Watching Korean Dramas and Movies for Fluency
Korean dramas and movies expose you to natural, real-life Korean. However, to maximize learning, you need to actively engage rather than passively watch.
A. The Right Way to Learn from K-Dramas
✅ Step 1: Watch with English subtitles first to understand the story.
✅ Step 2: Watch again with Korean subtitles and listen for words you recognize.
✅ Step 3: Pause, repeat, and shadow Korean dialogues.
✅ Step 4: Write down common phrases and try using them in real conversations.
🔹 Recommended Korean Dramas for Learning:
- Beginner-Friendly: "My ID is Gangnam Beauty" (simple dialogue)
- Intermediate: "Reply 1988" (real-life conversations)
- Advanced: "Itaewon Class" (fast-paced, business Korean)
5. Joining Korean Language Communities
Surrounding yourself with Korean learners and native speakers accelerates progress.
A. Join Online and Offline Korean Communities
✅ Reddit – r/Korean (for learning tips)
✅ Facebook Groups – Search “Learn Korean” groups
✅ Local Language Meetups – Find through Meetup.com
✅ KakaoTalk Open Chats – Many Korean learners practice here
B. Challenge Yourself with a 30-Day Korean Speaking Challenge
- Speak only Korean for 10 minutes a day.
- Record daily progress and review mistakes.
- Increase duration over time.
Achieving Fluency Through Active Speaking and Listening
Mastering listening and speaking in Korean requires consistent exposure and practice. The key is to engage daily, whether through listening to native speakers, mimicking pronunciation, practicing conversations, or immersing yourself in Korean media.
By applying the strategies in this section, you will notice significant improvements in your ability to understand and communicate in Korean.
Step 5: Strengthening Your Korean Reading and Writing Skills
Developing reading and writing skills in Korean is crucial for achieving overall language fluency. While speaking and listening are essential for communication, reading and writing help learners grasp complex grammar structures, expand vocabulary, and engage with Korean literature, news, and online content.

This section covers effective techniques to improve reading speed, comprehension, and writing skills while ensuring proper grammar usage.
1. Improving Your Korean Reading Skills
Reading in Korean allows you to encounter real-world sentence structures, idiomatic expressions, and cultural references. To improve comprehension and fluency, it is essential to start with simple texts and gradually move toward complex materials.
A. Choosing the Right Reading Materials
Selecting the right reading materials based on your proficiency level helps you progress without feeling overwhelmed.
| Level | Recommended Reading Material | Why It’s Useful |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Children's books, webtoons, simple dialogues | Short, repetitive sentences reinforce vocabulary |
| Intermediate | Korean news websites (Naver News, Daum), short stories | Introduces formal grammar and real-world expressions |
| Advanced | Korean novels, research papers, historical texts | Expands knowledge of complex sentence structures |
🔹 Best Websites for Korean Reading Practice:
- Naver Webtoons (네이버 웹툰): Fun, easy-to-follow visual stories.
- Naver Kids (네이버 키즈): Beginner-friendly articles with audio support.
- Soompi (for entertainment news): Korean pop culture articles with simple sentence structures.
B. Reading Korean Using the Extensive Reading Method
Extensive reading focuses on reading a lot of Korean text without stopping to translate every word.
✅ Step 1: Read a passage without a dictionary – focus on the overall meaning.
✅ Step 2: Underline unfamiliar words and try to guess their meanings from context.
✅ Step 3: Look up essential words only if they appear multiple times.
✅ Step 4: Summarize the passage in your own words to reinforce comprehension.
🔹 Tip: Start with graded readers (books written specifically for language learners) before moving to native materials.
C. Practicing with Speed Reading Techniques
Speed reading in Korean helps with fluency and confidence when reading large amounts of text.
✅ Chunking: Instead of reading word by word, read in phrases or groups of words.
✅ Scanning: Look for keywords and main ideas without reading every single word.
✅ Reading Aloud: Helps reinforce vocabulary and improve pronunciation.
2. Enhancing Your Korean Writing Skills
Writing in Korean reinforces sentence structure, vocabulary recall, and grammar rules. Many learners struggle with writing because Korean sentence order differs from English, and written Korean uses more formal expressions.
A. Learning Common Sentence Structures
Korean follows a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) structure, which differs from the English Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) pattern.
🔹 Example:
✅ English (SVO): "I eat an apple."
✅ Korean (SOV): "나는 사과를 먹어요." (I an apple eat.)
🔹 Common Writing Mistakes to Avoid:
❌ Directly translating from English (word order issues).
❌ Forgetting topic markers like 은/는, 이/가.
❌ Using informal language in formal writing.
B. Practicing Writing with Sentence Building Exercises
🔹 Beginner Level: Write simple diary entries using basic sentences.
🔹 Intermediate Level: Try summarizing short news articles.
🔹 Advanced Level: Write formal essays or blog posts in Korean.
✅ Daily Writing Challenge: Write three sentences per day in Korean and gradually increase complexity.
✅ Use AI tools like Grammarly for Korean or Papago's AI writing assistant to check grammar.
C. Mastering Korean Essay Writing
For academic or professional writing, it’s essential to structure your writing properly.
✅ Essay Structure in Korean:
- Introduction (서론) – Introduce the topic.
- Body (본론) – Provide supporting details.
- Conclusion (결론) – Summarize key points.
🔹 Example of a Basic Korean Paragraph:
◆서론: 한국어를 배우는 것은 매우 중요합니다.(Learning Korean is very important.)본론: 한국어를 공부하면 한국 문화를 더 잘 이해할 수 있습니다. 또한, 한국에서 일하거나 여행할 때 매우 유용합니다.(By studying Korean, one can better understand Korean culture. Additionally, it is very useful for working or traveling in Korea.)결론: 그러므로, 많은 사람들이 한국어 공부를 시작해야 합니다.(Therefore, many people should start learning Korean.)
3. Using Digital Tools to Enhance Reading and Writing
A. Best Apps for Reading Korean
✅ LingQ: Helps with reading comprehension by providing instant translations.
✅ Satori Reader: Provides Korean texts with explanations of grammar points.
✅ Naver Dictionary: Offers example sentences and detailed word definitions.
B. Best Apps for Writing Practice
✅ HiNative: Allows learners to ask native speakers for writing corrections.
✅ LangCorrect: A platform where native speakers provide feedback on your writing.
✅ Tandem: Connects you with language exchange partners for writing improvement.
4. Joining Online Korean Writing Communities
Practicing writing with real feedback helps improve fluency.
✅ r/Korean on Reddit: A great place to post writing samples for feedback.
✅ HelloTalk Writing Section: Lets native speakers correct your sentences.
✅ Facebook Groups for Korean Learners: Some groups focus on writing exercises.
C. Set a Weekly Writing Goal
- Week 1: Write a short diary entry in Korean (2-3 sentences).
- Week 2: Write a short paragraph about your daily routine.
- Week 3: Write a restaurant review in Korean.
- Week 4: Write a letter or email in Korean.
Becoming Proficient in Reading and Writing Korean
Mastering reading and writing in Korean requires consistent practice and exposure to native content. By following these steps, you will:
✅ Read Korean texts with ease using structured methods.
✅ Write grammatically correct sentences with natural flow.
✅ Engage in meaningful written communication with native speakers.
Step 6: Mastering Korean Grammar and Sentence Structure
Grammar plays a crucial role in understanding and constructing meaningful sentences in Korean. Unlike English, Korean grammar follows distinct word order, honorifics, and verb conjugation rules that require dedicated practice. This section provides a structured approach to mastering Korean grammar, verb conjugations, and sentence construction, ensuring clear and accurate communication.
1. Understanding Korean Sentence Structure
Korean follows a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) word order, which is different from the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) structure used in English.
🔹 Example:
✅ English (SVO): I eat an apple.
✅ Korean (SOV): 나는 사과를 먹어요. (I an apple eat.)
A. Key Elements of Korean Sentences
To construct grammatically correct sentences, it is essential to understand the key components:
| Element | Korean Example | Translation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject (주어) | 저는 학생입니다. | I am a student. | Indicates the topic of the sentence. |
| Object (목적어) | 저는 한국어를 공부해요. | I study Korean. | The action is being performed on this element. |
| Verb (동사) | 저는 책을 읽어요. | I read a book. | The main action of the sentence. |
| Adjective (형용사) | 날씨가 좋아요. | The weather is good. | Describes a noun. |
| Particles (조사) | 책을 읽어요. | (I) read a book. | Essential markers for meaning (e.g., 은/는, 이/가, 을/를). |
2. Learning Essential Korean Grammar Rules
Korean grammar can seem challenging at first, but breaking it into key concepts makes it easier to grasp.
A. Korean Particles (조사) and Their Functions
Particles indicate the relationship between words in a sentence.
| Particle | Usage | Example Sentence | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 은 / 는 | Topic marker | 저는 학생이에요. | I am a student. |
| 이 / 가 | Subject marker | 날씨가 좋아요. | The weather is nice. |
| 을 / 를 | Object marker | 책을 읽어요. | I read a book. |
| 에 | Location / Time | 학교에 가요. | I go to school. |
| 에서 | Location of action | 도서관에서 공부해요. | I study in the library. |
B. Verb Conjugation Rules
Korean verbs change form based on tense and politeness level.
🔹 Verb Conjugation in Present Tense
| Verb Root | Polite Form (아요 / 어요) | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| 가다 (to go) | 가요 | 저는 학교에 가요. (I go to school.) |
| 먹다 (to eat) | 먹어요 | 저는 밥을 먹어요. (I eat rice.) |
| 읽다 (to read) | 읽어요 | 저는 책을 읽어요. (I read a book.) |
🔹 Verb Conjugation in Past Tense
| Verb Root | Past Form (았어요 / 었어요) | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| 가다 (to go) | 갔어요 | 저는 어제 학교에 갔어요. (I went to school yesterday.) |
| 먹다 (to eat) | 먹었어요 | 저는 점심을 먹었어요. (I ate lunch.) |
| 배우다 (to learn) | 배웠어요 | 저는 한국어를 배웠어요. (I learned Korean.) |
🔹 Verb Conjugation in Future Tense
| Verb Root | Future Form (ㄹ 거예요) | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| 가다 (to go) | 갈 거예요 | 저는 내일 갈 거예요. (I will go tomorrow.) |
| 먹다 (to eat) | 먹을 거예요 | 저는 저녁을 먹을 거예요. (I will eat dinner.) |
C. Honorifics and Politeness Levels
Korean has different levels of politeness depending on the situation and whom you are speaking to.
| Politeness Level | Example Sentence | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Casual (반말) | 밥 먹었어? (Did you eat?) | Friends, younger people |
| Polite (존댓말) | 밥 먹었어요? (Did you eat?) | Strangers, acquaintances |
| Formal (격식체) | 식사하셨습니까? (Have you eaten?) | Business, elders, formal settings |
🔹 Key Honorific Expressions:
- 주다 (to give) → 드리다 (formal).
- 있다 (to have) → 계시다 (formal).
- 먹다 (to eat) → 드시다 (formal).
3. Common Sentence Patterns to Practice
Practicing sentence patterns helps you form correct sentences naturally.
A. Expressing Likes and Dislikes
✅ 저는 한국어 공부하는 것을 좋아해요. (I like studying Korean.)
✅ 저는 매운 음식을 싫어해요. (I dislike spicy food.)
B. Making Requests and Offers
✅ 물 한 잔 주세요. (Please give me a glass of water.)
✅ 도와드릴까요? (Shall I help you?)
C. Asking for Permission
✅ 화장실 가도 돼요? (May I go to the bathroom?)
✅ 사진 찍어도 괜찮아요? (Is it okay to take a photo?)
D. Expressing Ability or Inability
✅ 저는 한국어를 말할 수 있어요. (I can speak Korean.)
✅ 저는 피아노를 칠 수 없어요. (I can't play the piano.)
E. Talking About Experiences
✅ 한국에 가 본 적이 있어요. (I have been to Korea before.)
✅ 김치를 먹어 본 적이 없어요. (I have never tried kimchi.)
4. Using Grammar Books and Online Resources
To reinforce your grammar skills, consider using Korean grammar books and digital tools.
🔹 Recommended Grammar Books:
- "Korean Grammar in Use" (Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced) – A comprehensive guide with examples.
- "Essential Korean Grammar" by Laura Kingdon – Covers common grammar rules with exercises.
🔹 Best Online Grammar Resources:
- Talk to Me in Korean (TTMIK): Offers free grammar lessons.
- How to Study Korean: Detailed explanations and structured lessons.
- Sejong Korean Grammar Guide: Developed by the King Sejong Institute.
Mastering Korean Grammar Efficiently
Learning Korean grammar and sentence structure requires consistent practice and exposure to native content. By following structured learning techniques, you will:
✅ Understand and use correct sentence structures.
✅ Conjugate verbs accurately based on tense and politeness.
✅ Communicate effectively in both casual and formal settings.
Step 7: Developing Korean Speaking and Pronunciation Skills
Mastering spoken Korean requires a combination of correct pronunciation, active listening, and consistent practice with native speakers. This section provides a structured approach to improving Korean pronunciation, fluency, and conversational skills effectively.

1. Understanding Korean Pronunciation Rules
Korean pronunciation differs significantly from English, with unique consonants, vowels, and sound changes that affect fluency.
A. Mastering Korean Vowels and Consonants
Korean has 10 basic vowels, 11 compound vowels, and 14 consonants that combine to form words.
🔹 Common Pronunciation Challenges for Learners:
| Korean Sound | Challenge | Example Word | Correct Pronunciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ㄹ (rieul) | Between R/L | 나라 (country) | Not a hard "R" or "L" |
| ㅂ, ㅍ, ㅃ | Soft and aspirated sounds | 바보 (fool), 파도 (wave) | Slight puff of air |
| ㅊ vs. ㅈ | Strong vs. Soft | 친구 (friend), 자전거 (bicycle) | "ch" is stronger than "j" |
| ㅡ (eu) | No English equivalent | 크다 (big) | Mouth slightly closed |
| ㅗ vs. ㅓ | Different vowel placements | 보다 (to see) vs. 버스 (bus) | "O" is rounder, "eo" is deeper |
B. Learning Sound Changes in Spoken Korean (음운 변화)
Certain sounds change when words are spoken naturally.
| Sound Change | Rule | Example | Correct Pronunciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batchim (받침) Pronunciation | Final consonants sound different | 꽃 (flower) | Pronounced as "kkot" (no release) |
| Linking Sounds (연음화) | Final consonant moves to next syllable | 집에 (at home) | Pronounced as "지베" (jibe) |
| Nasalization (비음화) | Certain sounds become nasal | 학교 (school) | Pronounced as "학꾜" (hak-gyo) |
| Tensing (경음화) | Some sounds become tense | 한국말 (Korean language) | Pronounced as "한궁말" (han-gung-mal) |
2. Effective Techniques to Improve Speaking Skills
A. Shadowing Native Speakers
🔹 What is shadowing?
- Listening to native Korean speakers and repeating their words immediately.
- Helps with intonation, rhythm, and fluency.
🔹 How to practice shadowing:
- Choose short dialogues from Korean dramas, news, or YouTube channels.
- Listen carefully and repeat exactly as the speaker says it.
- Record yourself and compare with native pronunciation.
🔹 Recommended Resources:
- Talk to Me in Korean (TTMIK) Podcasts
- KBS News (for formal pronunciation)
- Korean dramas with subtitles (e.g., "Crash Landing on You")
B. Practicing with a Language Partner
Speaking with a native Korean or language partner enhances confidence and real-world conversation skills.
🔹 Where to find Korean language partners?
| Platform | Features |
|---|---|
| HelloTalk | Chat with native Korean speakers for free. |
| Italki | Find professional Korean tutors. |
| Tandem | Language exchange with Koreans. |
| Speaky | Connect with Korean learners and natives. |
🔹 Tips for effective conversation practice:
- Start with self-introduction: "안녕하세요, 저는 [your name]입니다." (Hello, I am [your name].)
- Ask basic questions: "어디에서 왔어요?" (Where are you from?)
- Use role-play scenarios: Practice ordering food, asking for directions, or shopping in Korean.
C. Using Speech Recognition Tools
Speech recognition tools help with correcting pronunciation mistakes and improving fluency.
🔹 Best Apps for Pronunciation Practice:
| App Name | Features |
|---|---|
| Google Translate (Korean voice input) | Check pronunciation accuracy. |
| Forvo | Listen to native pronunciation of words. |
| Pimsleur Korean | Interactive pronunciation practice. |
| LingQ | AI feedback on speaking accuracy. |
🔹 How to use speech recognition for improvement?
- Speak into the app and check if it correctly transcribes your words.
- Compare your pronunciation with a native speaker's version.
- Adjust and repeat difficult words until pronunciation improves.
3. Building Fluency through Daily Speaking Practice
A. Thinking in Korean
Instead of translating from English to Korean, practice thinking directly in Korean.
🔹 How to train your brain to think in Korean?
- Describe objects around you in Korean (e.g., "이것은 책이에요." – This is a book).
- Mentally form sentences about daily activities (e.g., "나는 지금 커피를 마셔요." – I am drinking coffee now).
- Write a daily journal in Korean to reinforce sentence formation.
B. Joining Korean Speaking Clubs
Regular participation in Korean-speaking communities can boost fluency.
🔹 Where to find speaking clubs?
- Reddit (r/Korean) – Discussion forums.
- Facebook Groups (Korean Language Exchange) – Virtual speaking meetups.
- Meetup.com (Korean Language Events) – Local and online events.
- Discord Korean Learning Servers – Practice with learners worldwide.
🔹 Recommended Speaking Exercises:
- 10-minute daily conversations on a random topic.
- Record yourself speaking and review it weekly.
- Mimic Korean radio hosts to improve speech rhythm.
4. Using Korean Dramas, K-Pop, and Podcasts for Speaking Skills
Engaging with Korean media enhances speaking fluency in a fun and interactive way.
A. Learning with Korean Dramas
- Watch with Korean subtitles to reinforce listening and pronunciation.
- Pause and repeat dialogues to mimic native speakers.
- Practice emotional expressions used in dramas.
✅ Recommended Dramas for Beginners:
- "미생" (Misaeng) – Realistic workplace Korean.
- "도깨비" (Goblin) – Clear pronunciation and daily conversations.
- "내일" (Tomorrow) – Formal and informal speech usage.
B. Using K-Pop Songs for Pronunciation
- Sing along with lyrics to practice pronunciation and intonation.
- Break down lyrics to understand grammar and vocabulary.
- Focus on diction used by singers.
✅ Best K-Pop Songs for Learning Korean:
- "작은 것들을 위한 시" (Boy with Luv) – BTS
- "좋은 날" (Good Day) – IU
- "사랑을 했다" (Love Scenario) – iKON
C. Listening to Korean Podcasts
Podcasts improve listening comprehension and speaking rhythm.
🔹 Best Korean Podcasts for Learners:
| Podcast | Level |
|---|---|
| Talk to Me in Korean | Beginner to Advanced |
| KoreanClass101 | All levels |
| Naver Audio Clip | Intermediate to Advanced |
🔹 How to Use Podcasts for Speaking Practice?
- Listen to a short episode and note down difficult words.
- Repeat sentences aloud mimicking native speakers.
- Summarize the episode in Korean to reinforce learning.
Speaking Korean with Confidence
Improving Korean speaking and pronunciation takes dedication, but with consistent practice, you will:
✅ Pronounce Korean words accurately.
✅ Speak naturally using correct intonation.
✅ Hold conversations confidently in various situations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to learn Korean?
The time required to learn Korean depends on factors like your native language, study consistency, and learning methods. According to the Foreign Service Institute (FSI), Korean is a Category IV language, meaning it takes approximately 2,200 hours for English speakers to reach fluency. However, with immersive learning, daily practice, and active listening, you can achieve conversational fluency in 6–12 months.
2. Is Korean grammar difficult to learn?
Korean grammar is structured differently from English, making it challenging at first. Key differences include:
- Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) word order (e.g., "I apple eat" → 나는 사과를 먹어요).
- Honorifics to show respect (e.g., 먹다 → 드시다 for "to eat").
- Particles instead of prepositions (e.g., -은/는, -이/가, -을/를).
Despite these differences, once you understand sentence structures and verb conjugation rules, Korean grammar becomes easier to grasp.
3. What is the fastest way to learn Korean?
The fastest way to learn Korean involves immersion and consistency. Here’s an optimized approach:
✅ Learn Hangul (Korean alphabet) first – It only takes a few hours!
✅ Memorize essential vocabulary – Start with the 1,000 most common words.
✅ Practice speaking daily – Use language exchange apps (HelloTalk, iTalki).
✅ Watch K-dramas and listen to K-pop – Helps with pronunciation and listening.
✅ Use spaced repetition flashcards (Anki, Memrise) for vocabulary retention.
4. Is Hangul (Korean Alphabet) hard to learn?
No! Hangul (한글) is one of the easiest alphabets in the world. It was created in the 15th century by King Sejong to be logical and simple. You can learn all Hangul characters in a few hours by understanding:
- 14 basic consonants (ㄱ, ㄴ, ㄷ, etc.)
- 10 vowels (ㅏ, ㅓ, ㅗ, etc.)
- Syllabic structure (e.g., 한 = ㅎ + ㅏ + ㄴ)
With daily reading and writing, you can master Hangul within a week.
5. Should I learn Korean vocabulary or grammar first?
Both are important, but vocabulary should be your priority initially. Without words, even perfect grammar is useless. Here’s a recommended approach:
1️⃣ First, learn essential vocabulary (e.g., greetings, numbers, common nouns).
2️⃣ Then, understand basic grammar structures (e.g., sentence order, verb conjugation).
3️⃣ Finally, practice forming sentences using both.
6. Can I learn Korean without a tutor?
Yes, you can learn Korean without a tutor by using self-study methods and online resources:
- Beginner Level: Learn Hangul, use Duolingo, TTMIK (Talk To Me In Korean).
- Intermediate Level: Watch K-dramas, read webtoons, listen to podcasts.
- Advanced Level: Engage in language exchanges, write daily journals, and read news in Korean.
However, hiring a tutor for pronunciation and conversational practice can accelerate fluency.
7. What are the best apps to learn Korean?
Here are the top-rated apps for learning Korean:
✅ Duolingo – Gamified learning for beginners.
✅ Talk To Me In Korean (TTMIK) – Best for grammar and structured lessons.
✅ Memrise – Spaced repetition for vocabulary.
✅ HelloTalk – Chat with native speakers.
✅ Anki – Custom flashcards for memorization.
✅ Naver Dictionary – Best for Korean-English translations.
8. Is Korean harder to learn than Japanese or Chinese?
- Korean vs. Japanese: Korean grammar is similar to Japanese, but Korean pronunciation is easier.
- Korean vs. Chinese: Korean has fewer characters (Hangul) than Chinese (Hanzi), making it easier to read.
- Overall: Korean is easier than Chinese but on par with Japanese in terms of sentence structure.
9. How can I improve my Korean pronunciation?
✅ Listen to native speakers – Use K-dramas, K-pop, and podcasts.
✅ Practice shadowing – Repeat phrases immediately after hearing them.
✅ Record yourself speaking and compare it with native pronunciation.
✅ Learn correct vowel and consonant sounds – Some Korean sounds (like ㄹ) don’t exist in English.
10. Where can I practice speaking Korean?
✅ HelloTalk, Tandem – Chat with native speakers.
✅ iTalki, Preply – Hire affordable Korean tutors.
✅ Korean Meetup Groups – Find local language exchange events.
✅ Join Discord/Reddit Korean Language Groups.
11. How do I stay motivated while learning Korean?
✅ Set clear goals (e.g., "I want to hold a 10-minute conversation in Korean in 3 months").
✅ Track your progress (use apps like Notion, language journals).
✅ Engage with Korean content you love (e.g., K-dramas, webtoons, blogs).
✅ Find an accountability partner – Join online study groups.
✅ Celebrate milestones – Reward yourself when you master a new skill.
Conclusion: Mastering Korean with Consistency and Smart Strategies
Learning Korean is a rewarding journey that requires dedication, consistency, and the right learning techniques. Whether you are studying for travel, career opportunities, or personal interest, a structured approach can help you achieve fluency faster.
Key Takeaways:
✅ Start with Hangul – Master the Korean alphabet first.
✅ Build a strong vocabulary foundation – Learn the most common words and phrases.
✅ Understand grammar basics – Focus on sentence structure and verb conjugations.
✅ Practice daily immersion – Listen to K-pop, watch K-dramas, and read Korean content.
✅ Engage in conversations – Use language exchange apps and real-world practice.
✅ Stay consistent and track progress – Set goals, maintain a study schedule, and celebrate small wins.
Final Thoughts
While Korean may seem challenging at first, anyone can learn it with the right mindset and resources. The key is to immerse yourself in the language, make learning fun, and stay patient with your progress. Every new word you learn and every sentence you form brings you one step closer to fluency.
Start your Korean learning journey today, and before you know it, you’ll be confidently speaking, reading, and understanding the language!