Who Is the Father of Math? Origins, Legends, and Global Impact of Mathematics
Why This Question Still Fascinates Us
Ever Googled “Who Is the Father of Math?” You’re Not Alone.
Over 1,400 people search for "who is the father of math" every month—and that number keeps rising. It's a question that sounds straightforward but opens the door to centuries of discovery, debate, and even controversy in the world of mathematics.
A Personal Moment That Sparked a Lifelong Curiosity
I still remember the exact page of my old Class 6 math textbook. There it was, in bold letters:“Euclid is known as the Father of Geometry.”
That simple statement lit a fire in my young mind. “Wait, geometry has a father? Then who’s the father of all math?” I rushed to ask my teacher, searched through encyclopedias (this was before Google!), and found... conflicting answers.
That childhood question turned into a lifelong curiosity. And today, it's a curiosity shared by thousands around the globe—especially in 2025, when AI tools, data science, and digital education are redefining how we understand math and its origins.
Why the Question “Who Is the Father of Math?” Still Matters in 2025
In a world powered by algorithms and statistics, understanding the origins of mathematics is more important than ever. This isn’t just a historical footnote—it’s about honoring the foundations of everything from AI and quantum computing to finance and architecture.
The phrase “father of mathematics” doesn’t just point to one person. It invites us to explore:
- 👨🏫 Who is officially known as the father of math?
- 🌍 Were there other contributors from different cultures and civilizations?
- 🤖 Why does this question continue to be relevant in modern times?
Spoiler alert: While Euclid is often considered the "Father of Geometry," another name usually takes the crown when it comes to all of mathematics—and you'll meet him soon.
What This Article Will Cover
In this guide, we’ll walk you through:
- ✅ The person widely regarded as the father of mathematics
- 🌐 Contributions from Babylonian, Egyptian, Indian, Chinese, and Islamic mathematicians
- 📈 Why understanding the history of math helps us appreciate modern technology and innovation
So if you’ve ever asked:
- “Who is considered the father of math?”
- “Is it Archimedes or Euclid?”
- “Did ancient India contribute to mathematics?”You’re in the right place.
📌 Related Reading: Who Invented Math?
Who Is the Father of Math?
Short Answer: Archimedes is widely regarded as the father of mathematics due to his groundbreaking work in geometry, calculus, and mechanical engineering.
Why Archimedes Deserves the Title
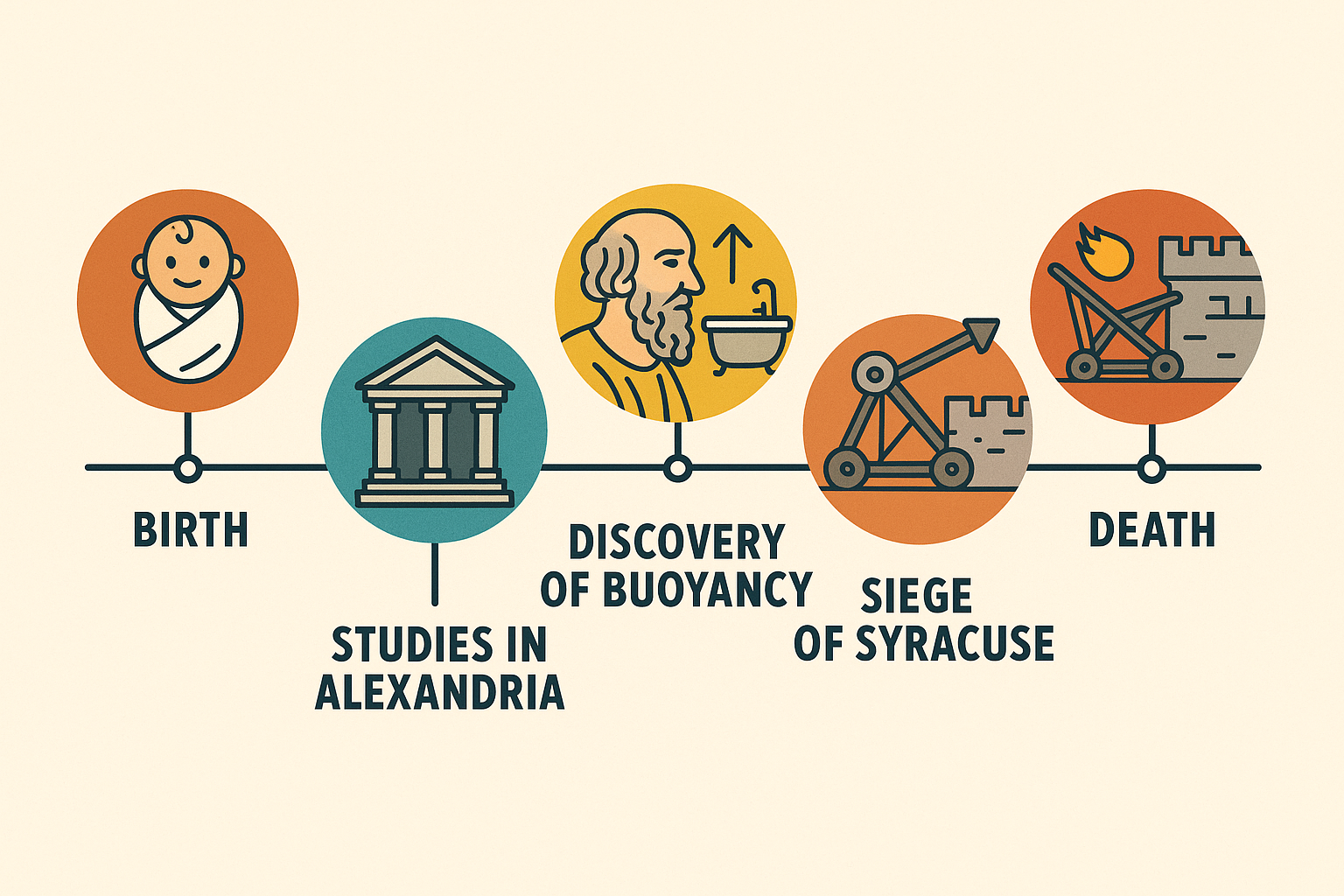
When we talk about the "father of mathematics," Archimedes’ name surfaces again and again — and for good reason. Born in 287 BCE in the ancient city of Syracuse, Archimedes revolutionized the way we think about numbers, shapes, and motion. His work laid the foundation for modern calculus, centuries before Isaac Newton and Leibniz would formalize it.
From calculating the volume of irregular objects using water displacement (the famous "Eureka!" moment) to inventing war machines that protected his city from Roman invasion, Archimedes was much more than a mathematician — he was a visionary thinker and engineer.
◆💬 Pull Quote: “Give me a place to stand, and I will move the Earth.” — Archimedes
Archimedes' contributions include:
- Developing the concept of infinitesimals (a precursor to integral calculus)
- Inventing the Archimedean screw (still used today for irrigation)
- Formulating the laws of levers and buoyancy
- Creating formulas to calculate areas and volumes in geometry
Relevant:
Who Is the Father of Math in the World?
When we ask "Who is the father of math in the world?", we're not just seeking one name—we’re exploring a mosaic of global mathematical evolution. While Archimedes is widely celebrated, different cultures revere their own pioneers who laid foundational stones for modern mathematics.
India: Aryabhata – The Algebraic Astronomer
In 499 CE, Indian mathematician Aryabhata wrote the Aryabhatiya, a text that introduced concepts like zero, place value, and trigonometric functions. His calculation of π (pi) was remarkably accurate, and his astronomical models placed the Earth rotating on its axis—centuries before Galileo.Aryabhata's work continues to influence both mathematical theory and satellite missions in India.
Greece: Euclid – The Father of Geometry
Often called the "father of geometry," Euclid authored The Elements, a 13-book treatise compiling all known knowledge of geometry at the time. His axiomatic approach became the foundation for logical proofs and modern mathematics.
Babylon and Egypt: The Unsung Calculators
Long before Euclid or Aryabhata, the Babylonians and Egyptians were crunching numbers. Babylonian clay tablets (as early as 1800 BCE) show an understanding of quadratic equations, while Egyptian texts like the Rhind Papyrus illustrate arithmetic used in construction and agriculture.Though less theoretical, their practical math influenced future civilizations.
Global Contributions
Rather than crediting one "founder," it’s more accurate to honor the diversity of mathematical origins:
Mathematical Titans by Region
| Region | Name | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| India | Aryabhata | Zero, π approximation, astronomy |
| Greece | Euclid | Geometry, axioms, logical proofs |
| Babylon | Anonymous | Algebraic tables, base-60 system |
| Egypt | Scribes | Fractions, geometry for pyramids |
🧠 Modern takeaway: Math is a global language—shaped by many dialects.
🔗 Related Read: How to Study for the LSAT
Who Is the Indian Father of Maths?
Answer: Aryabhata is widely regarded as the Indian father of mathematics.
Born in 476 CE, Aryabhata was a pioneering mathematician and astronomer whose works shaped the mathematical landscape of not only India but also the entire world. His groundbreaking contributions include:
Aryabhata’s Mathematical Legacy
- Invention of Zero: While the concept of zero existed earlier in different cultures, Aryabhata was among the first to use it systematically in calculations.
- Trigonometric Functions: He introduced sine (jya), cosine (kojya), and versine (utkrama-jya), laying the foundation for modern trigonometry.
- Decimal Place Notation: Aryabhata developed the place value system using base-10, which is still in use today.
- π (Pi) Approximation: He calculated π (pi) to four decimal places — remarkably accurate for his time.
◆“Add, subtract, multiply, divide — Aryabhata did it all before it was cool.”
Myth-Busting Box: Aryabhata vs. Brahmagupta
| Aryabhata | Brahmagupta |
|---|---|
| Introduced zero as a placeholder and concept | Formalized the rules for zero in operations |
| Known for Aryabhatiya | Known for Brahmasphutasiddhanta |
| Born: 476 CE | Born: 598 CE |
🧩 Did You Know?
Aryabhata composed his entire text Aryabhatiya in verse form using Sanskrit slokas — making mathematics poetic centuries before it became cool.
Q: Who invented zero?
A: Aryabhata laid the foundational concept of zero as a placeholder, but Brahmagupta was the first to define its operations formally around 628 CE.
Contextual Learning
Who Is Known as the Father of Modern Math?
Answer: René Descartes
If ancient math had its titans, modern math found its architect in René Descartes — a 17th-century French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician. Often hailed as the father of modern mathematics, Descartes laid the foundation for much of the math we use today — not just in theory but in practice.
Why Descartes Is Called the Father of Modern Mathematics
René Descartes revolutionized mathematics by introducing the Cartesian coordinate system — yes, the very X and Y axes we use to plot graphs. This seemingly simple innovation merged algebra and geometry, giving birth to analytic geometry, a discipline that paved the way for calculus, engineering, physics, and even computer graphics.
His work helped move mathematics from the abstract to the visual, providing tools that are still used in everything from economics charts to AI modeling.
◆“I think, therefore I am... and I measure, therefore I graph.”
Contributions That Cemented Descartes' Legacy
- Cartesian Plane: Connected algebra with geometry.
- Algebraic Geometry: Enabled plotting of equations as shapes.
- Foundational Logic: Influenced both mathematics and philosophy.
- Influence on AI: Descartes’ emphasis on rationalism and logic inspired early algorithmic thinking — cornerstones of artificial intelligence.
◆Did You Know? Descartes’ analytic geometry concepts are used in machine learning algorithms and AI decision trees today!
Related Questions
Q: Why is Descartes called the father of modern math?
A: Because he introduced the Cartesian coordinate system, blending algebra with geometry and shaping modern analytical methods.
Q: What is the Cartesian plane?
A: A graph system that allows mathematical equations to be represented visually on an X and Y axis.
Related:
- Digital Marketing Courses – See how Cartesian logic applies to data analytics in marketing!
Who Is the Father of “The Math”? — Grammatical Curiosity
Answer: Archimedes is universally acknowledged as the father of mathematics — even if the phrasing “the math” might sound grammatically off.
Why “The Math”?
The phrase “the math” isn’t wrong — just regionally or culturally different. It's often used by non-native English speakers or in casual conversations. For instance:
| Phrase | Common Usage | Region/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Math | “I enjoy math.” | USA, Canada |
| The Math | “He is great at the math.” | Informal, ESL contexts |
| Mathematics | “She’s pursuing a degree in mathematics.” | UK, formal/academic English |
Who Has the Best Math? (Debate-Style Section)
Answer: According to the most recent global assessments, countries like Singapore, China (especially Shanghai and Beijing), and Japan consistently outperform others in mathematics proficiency. The U.S. still lags behind in international rankings despite its technological advancements and education investments.
Top Countries Ranked by Math Scores (2023–2024)
Here’s how countries stack up in the latest global math assessments:
| Country | PISA Math Score (2022) | TIMSS Grade 8 Math (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 575 | 625 |
| 🇨🇳 China (B-S-J-Z) | 561 | 609 |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 536 | 594 |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 527 | 588 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 478 | 515 |
📝 Note: PISA = Programme for International Student Assessment; TIMSS = Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study.
🌍 Why Do Some Countries Excel?
Countries like Singapore and China emphasize:
- 🔢 Mastery-based learning from an early age
- 🧑🏫 Rote memorization + problem-solving hybrid systems
- 📚 Heavily structured curriculum
- 👪 Strong parental involvement and academic expectations
Meanwhile, countries like the U.S. focus more on exploratory learning and critical thinking — valuable, but less reflected in standardized tests.
📌 Curious how your state compares? Check out Where Does Florida Rank in Education K–12?
Global Math Rankings at a Glance
- PISA and TIMSS are gold standards in assessing global math skills.
- Singapore has led the world in both assessments for over a decade.
- U.S. performance has remained flat, showing room for reform.
🧠 Insight: Scoring high in math isn’t just about intelligence — it's about educational culture, priorities, and teaching methods.
Why Should Students Know This?
Understanding who the "Father of Math" is—and the broader historical context of mathematical development—is more than just trivia. It builds cultural literacy, critical thinking, and academic versatility.
Builds Historical Awareness and Academic Curiosity
Learning about the evolution of mathematics connects students to a global intellectual tradition. From Aryabhata’s astronomical calculations to Euclid’s geometric proofs, these figures offer more than equations—they offer stories. Understanding where math came from helps students appreciate why it matters today.
Great Icebreaker in College Essays, Exams, and Interviews
Many competitive college essays and scholarship interviews look for personal insights and curiosity. Referencing the origin of math or a favorite historical figure in the field can demonstrate passion and interdisciplinary thinking—qualities every academic institution values.
Bonus Tip: Teachers Can Use This for Engagement in ESL or STEM Classes
Educators in both STEM and ESL environments can leverage this topic as a dynamic tool. It helps humanize the subject, promote discussion, and encourage cultural understanding—perfect for sparking interest and engagement.
Further Learning:
Timeline of the Mathematic Masters
Mathematics didn’t begin with calculators—it evolved over thousands of years. This scrollable timeline captures the greatest milestones and minds that shaped math as we know it.
🕰️ From Tally Marks to TensorFlow
- Prehistoric Era – Early humans used tally marks on bones and cave walls for counting, marking the birth of mathematical thought.
- c. 1800 BCE – Babylonian Math – Developed a base-60 (sexagesimal) number system. Their clay tablets show advanced arithmetic and early algebra.
- 300 BCE – Euclid (Greece) – Known as the "Father of Geometry", his book Elements shaped math education for centuries.
- 476 CE – Aryabhata (India) – Introduced concepts of zero, place value, and accurate calculations of π and solar years.
- 1637 – René Descartes (France) – Created Cartesian coordinates and bridged algebra with geometry.
- 1800s – Carl Friedrich Gauss (Germany) – Revolutionized number theory, statistics, and electromagnetism.
- Today – Data Scientists – Modern-day mathematicians apply statistical modeling, machine learning, and big data to solve real-world problems.
Further Learning:
❓ FAQs: Ancient Mathematicians You Should Know
1. Who is considered the first mathematician in history?
🔍 Historians often credit Thales of Miletus (624–546 BCE) as the first known mathematician for introducing deductive reasoning in geometry.However, earlier mathematical knowledge existed in Babylonian and Egyptian cultures.
2. What did Aryabhata contribute to mathematics?
🇮🇳 Aryabhata was an Indian mathematician and astronomer who introduced the concept of zero, accurate formulas for π, and advanced trigonometry. His work influenced global mathematics for centuries.
3. Why is Euclid called the "Father of Geometry"?
📏 Euclid’s book Elements systematized geometry into axioms and theorems. This structured approach formed the basis of modern mathematics education.
4. What role did mathematics play in ancient civilizations?
🧱 Math was used in agriculture, architecture, astronomy, and trade. Civilizations like the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Chinese used math to solve practical problems—long before it became academic.
5. How is ancient math relevant in modern education?
📚 Concepts like algebra, geometry, and even binary logic have roots in ancient discoveries. They’re now core to modern fields like engineering, data science, and computer science.
📎 Want to dive deeper into how these concepts are applied today?
Check out: What Is the Primary Function of Dynamic Study Modules?
Conclusion: From Clay Tablets to Code
The journey of mathematics is not just about numbers — it’s about human curiosity, creativity, and the constant quest to understand the universe. From Aryabhata’s astronomy to Euclid’s geometry and Gauss’s genius, ancient mathematicians laid the foundation for everything from skyscrapers to smartphones.
✨ Whether you're a student prepping for exams or a teacher designing a lesson plan, knowing these iconic thinkers adds depth to your learning and storytelling.
